Evotec’s in vitro transcription/translation (IVTT) platform provides fast, scalable cell-free protein expression to accelerate drug discovery and functional studies. The platform enables high-throughput screening of thousands of proteins, including biologics and enzymes, and supports milligram-scale production for downstream applications. Integrated with purification, quality control, and activity assays, Evotec’s IVTT services deliver rapid, reproducible expression of difficult-to-produce proteins, offering flexible solutions for research, structural biology and therapeutic development.
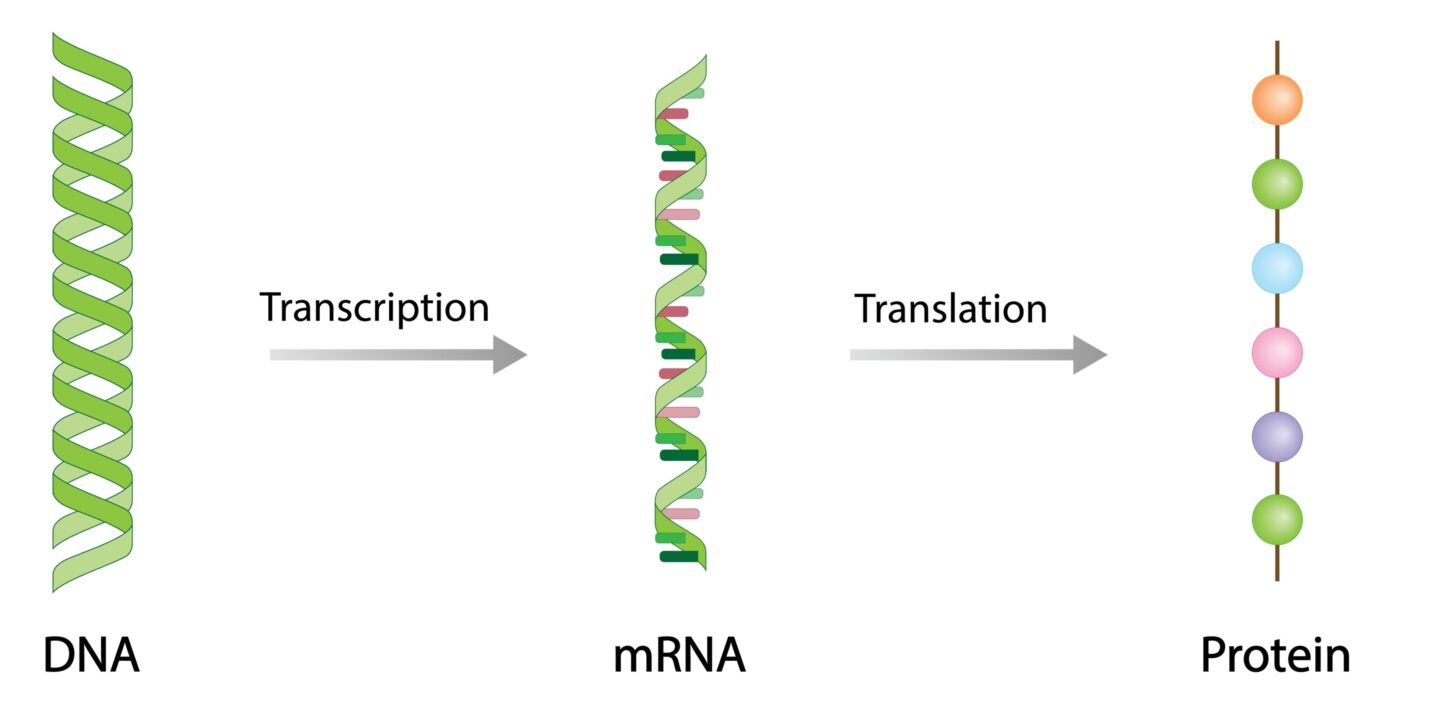
DNA to protein synthesis through transcription and translation
Evotec Expertise
Evotec’s in vitro transcription/translation expertise combines high-throughput cell-free expression with integrated purification and analysis, enabling rapid, scalable production of functional proteins.
- Validated IVTT components offered as kits, single proteins, or reactions
- High-throughput screening for thousands of proteins, biologics and enzymes
- Integrated purification for small-scale protein recovery
- Assay and activity integration for comprehensive functional data
- Scalability to milligram production for downstream research and development
Featured In Vitro Transcription/Translation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is IVTT expression?
- In vitro transcription/translation (IVTT) is a cell-free protein synthesis method where DNA or mRNA is translated into proteins using ribosomes, amino acids, and tRNAs outside living cells.
Q: What are the advantages of IVTT expression?
- Speed & efficiency – proteins produced within hours, faster than in vivo expression
- Versatility – supports difficult-to-express proteins and interaction studies
- Open system – easy optimization and addition of folding enhancers
- High-throughput screening – parallel testing of multiple constructs
- Accessibility – minimal specialized equipment required
- Labeling options – incorporation of isotopes or unnatural amino acids
Q: What are the limitations of IVTT expression?
- Limited post-translational modifications compared to living cells
- Lower protein yields in some systems versus in vivo expression
- No endogenous membranes, limiting certain protein types
Q: What are common applications of IVTT expression?
- Studying protein–protein and protein–nucleic acid interactions
- Rapid protein production for functional or mutant analysis
- Folding and stability studies for complex proteins
- Therapeutic development, supporting drug discovery and biologics research