BCRP substrate identification is in our portfolio of in vitro drug transporter services. Cyprotex delivers consistent, high quality data in line with our published transporter strategy review, for either your early stage screening projects or your later stage regulatory studies according to FDA, EMA, PMDA and ICH guidance.
Introduction
In vitro BCRP substrate identification service:
- BCRP (breast cancer resistance protein; ABCG2) is an important efflux transporter. It is expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidney, brain endothelium, mammary tissue, testis, and placenta1.
- The ITC1, the EMA guideline2 and the FDA guidance3 recommend investigating BCRP due to the clinical importance of BCRP in the absorption and disposition of drugs. Furthermore, clinically relevant genetic polymorphisms of ABCG2 have been shown to impact the pharmacokinetics and toxicity of marketed drugs, and underlie the ethnic differences in exposure between Japanese and Caucasian populations for some substrate drugs.
- Caco-2 cells express BCRP. The EMA2 and FDA3 regulatory guidelines recommend polarized Caco-2 cell monolayers (the “gold-standard” methodology) as as one of the preferred methods for evaluating the role of BCRP in the efflux of new chemical entities.
- Caco-2 cells are a superior test system for the correct identification of polar BCRP substrates as other systems such as MDCK-BCRP cells can give false negatives for hydrophilic molecules due to not expressing the basolateral OST alpha uptake transporter needed to facilitate their traversing the membrane in order to interact with BCRP as substrates4.
- The assay investigates bidirectional transport across the cell monolayer in the presence and absence of the selective BCRP reference inhibitor, fumitremorgin C, to determine if active efflux is occurring, and whether this efflux is mediated by BCRP.
- Where Caco-2 cell assays indicate a compound has inherently low passive permeability, then BCRP expressing inside-out membrane vesicles can be used as an alternate in vitro test system to identify BCRP substrates and reduce the potential risk of false negatives from the polarized cell monolayer system for such compounds.
Protocol
"Gold-standard" Cellular BCRP Substrate Identification Assay Protocol
Inside-Out Membrane Vesicle BCRP Substrate Identification Assay Protocol
Data
Data from Cyprotex's Cellular BCRP Substrate Identification Assay
The expression and functional activity of BCRP in our Caco-2 cells were determined. Relative mRNA expression levels (relative to housekeeping gene) of the main transporters were analyzed by qRT-PCR. BCRP mRNA was expressed in the cells and had comparable relative expression levels with MDR1 (0.041 ± 0.011 for BCRP and 0.047 ± 0.014 for MDR1). Functional activity of BCRP was determined by investigating the inhibition of the BCRP substrate, estrone 3-sulfate, by a number of BCRP and P-gp inhibitors.
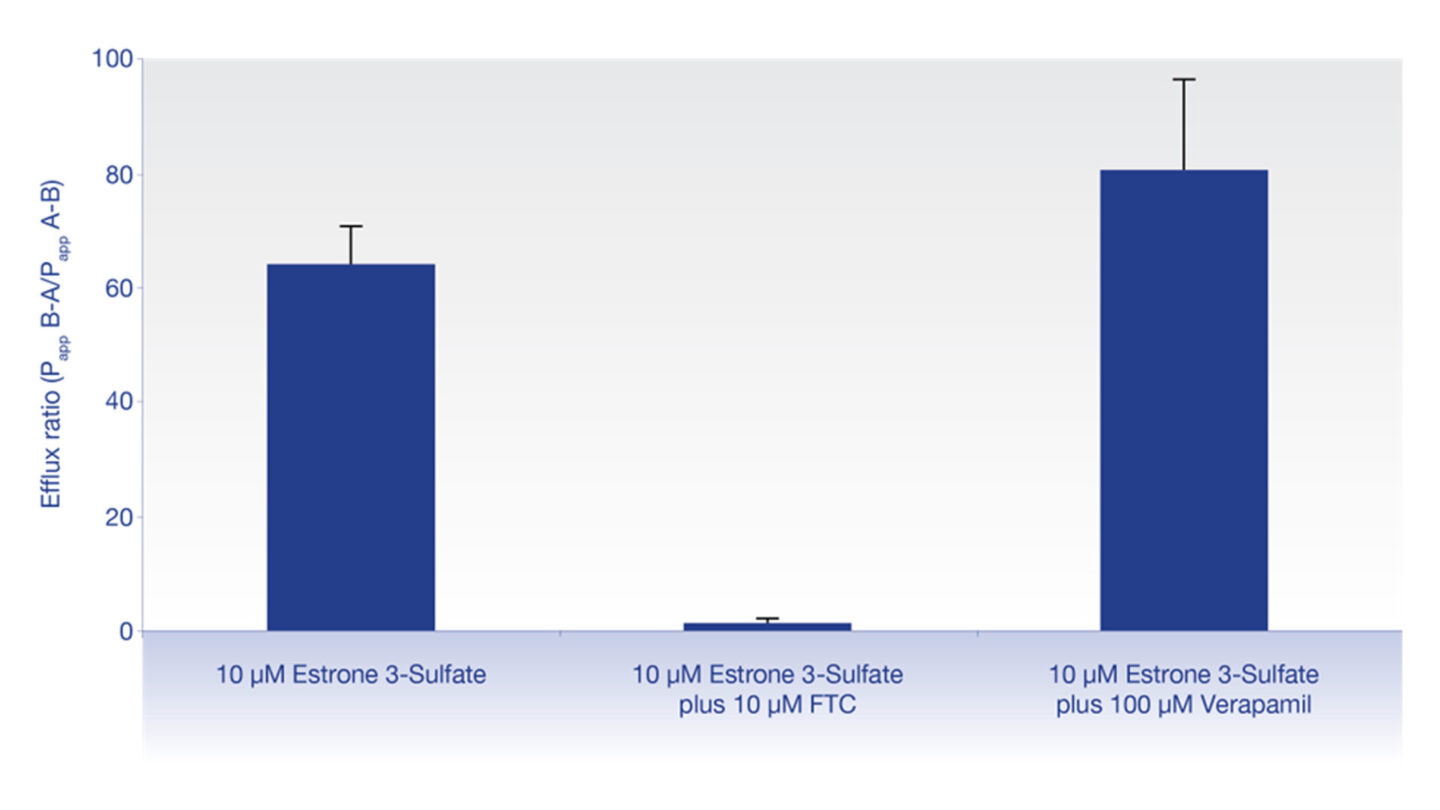
Figure 1
Graph showing effect of the selective BCRP inhibitor, fumitremorgin C (FTC) and the selective P-gp inhibitor, verapamil, on the efflux of the BCRP substrate, estrone 3-sulfate.
Estrone 3-sulfate efflux was not inhibited by the P-gp inhibitor, verapamil, but was inhibited by the selective BCRP inhibitor, fumitremorgin C (FTC), showing selectivity of estrone 3-sulfate as a BCRP substrate. Data show the mean ± standard deviation.
References
1) The International Transporter Consortium (2010) Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Disc 9; 215-236
2) The European Medicines Agency (EMA) Guideline on the Investigation of Drug Interactions (Adopted 2012)
3) FDA Guidance for Industry – In Vitro Drug Interaction Studies - Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions (January 2020)
4) Elsby R et al. (2023) Mechanistic in vitro studies indicate that the clinical drug-drug interactions between protease inhibitors and rosuvastatin are driven by inhibition of intestinal BCRP and hepatic OATP1B1 with minimal contribution from OATP1B3, NTCP and OAT3. Pharmacol Res Perspect 11(2); e01060
Downloads
- Cyprotex ADME Guide 5th Edition >
- Cyprotex DDI Regulatory Guide 3rd Edition >
- Cyprotex Transporter Strategy Guide >