Innovating drug discovery with next-generation proteomics
Significant hurdles are still faced in drug discovery, with most known disease targets being classified as “undruggable”. These lack the structural features ideal for small molecule binding, such as deep, well-defined ligand binding pockets. Instead, undruggable proteins often have flat or highly dynamic surfaces that lack obvious binding hotspots.
Next-generation proteomics is helping to overcome these challenges. The emergence of data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry (DIA-MS) techniques is one such example for discovering drugs for notoriously challenging targets. DIA-MS is an untargeted mass spectrometry approach that offers in-depth coverage of the proteome with high reproducibility, accuracy, and throughput.
This method not only identifies novel disease-relevant biomarkers and targets, but also enables the discovery of novel therapeutic compounds through fragment-based screening. In this approach, chemical probes can be screened against the entire proteome using DIA-MS. This MS-based technique precisely maps target-ligand interactions in relevant human cells and tissues.
In this blog, we discuss how fragment-based screening using DIA-MS drives the discovery of novel drug compounds, including covalent and reversible inhibitors. We also explore how Evotec is expanding the druggable proteome with its next-generation proteomics platforms, including high-throughput activity-based protein profiling (HT-ABPP), high-throughput photoaffinity labeling mass spectrometry (HT-PALMS), and ScreenPep™.
Discovering novel covalent fragments using a DIA-MS-based method
Covalent fragments hold the potential to drug the undruggable, with their ability to bind to shallow, cryptic, allosteric, or transient binding sites. By forming irreversible covalent bonds with their targets, these fragments offer high target occupancy, potency, and a prolonged duration of action.
Novel covalent fragments can be discovered using DIA-MS-based approaches, like activity-based protein profiling (ABPP). In ABPP, labeled chemical probes are screened against the entire proteome, with DIA-MS used to map target reactive sites and occupancy. This assesses probe specificity, identifying safe and potent hits, even for challenging or poorly characterized disease targets.
The possibilities of covalent fragment discovery are being taken a step further with Evotec’s high throughput ABPP (HT-ABPP) platform. Firstly, workflows are streamlined using a robotic liquid handling platform for peptide enrichment and clean-up. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) is used to assess ligand-target binding in vivo, with the ability to analyze many different human cell lines and primary cells.
This DIA-MS-based platform has high precision and speed, allowing for the consistent mapping of 87,000+ reactive cysteine sites on 15,800+ unique proteins, and 12,000+ distinct reactive lysine sites on 3,500+ unique proteins, with a throughput of up to 60 samples per day.
Designing reversible inhibitors using DIA-MS-based photoaffinity labeling
DIA-MS approaches are also powerful tools to identify reversible inhibitors. As suggested by their name, this type of drug binds reversibly with its target(s), typically via non-covalent bonds. Reversible fragments can bind to challenging targets, and in contrast to covalent drugs, temporary binding to off-targets helps reduce potential toxicity.
When combined with photoaffinity labeling, DIA-MS can discover novel reversible inhibitors. In this method, a library of photoreactive probes detect reversible ligand-target interactions. These probes contain a photoreactive diazirine group, plus a variable fragment, and an alkyne handle attached to a reporter or affinity tag. Following probe screening using DIA-MS, identified fragments can be structurally elaborated to optimize binding affinity, specificity, or activity.
High-throughput photoaffinity labeling mass spectrometry (HT-PALMS) platforms like Evotec’s are accelerating the discovery of safe and potent reversible compounds. Using advanced mass spectrometry, thousands of small molecule fragment-protein interactions can be mapped directly in human cells. Generated hits and their structurally elaborated analogs can be further profiled with tailored competitive assays to determine structure-activity relationships, identifying the most promising chemical starting point for your target of interest.
Enabling large-scale proteomics discovery
Recent advances in mass spectrometry-based proteomics are promising to take drug discovery even further, offering higher throughput, without compromising on coverage or precision. These advances are being driven by Evotec’s DIA-MS-based compound screening platform “ScreenPep™”. The platform integrates fast automation and parallelization, with the ability to process up to 300,000 samples per year.
ScreenPep has a fully automated workflow that encompasses cell culture, sample preparation, DIA-MS data acquisition, and data processing - ensuring consistent and reliable results. Additionally, ScreenPep can quantify various post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, and methylation, enhancing the ability to identify novel ligand-target interactions
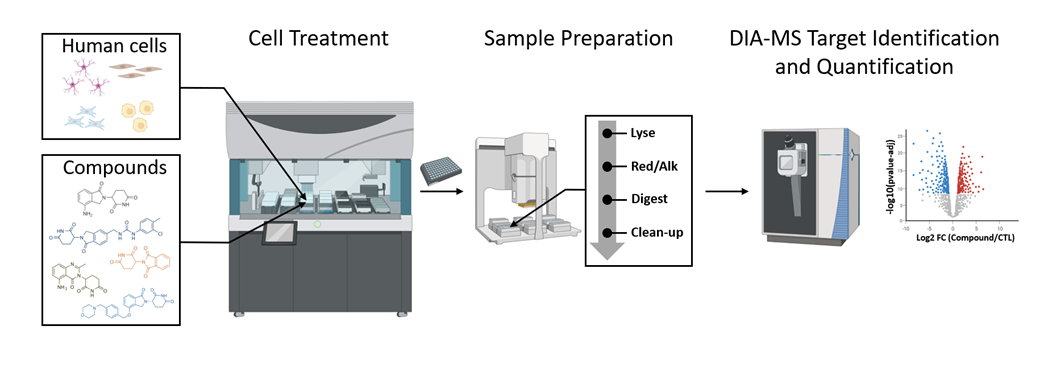
Figure 1: Overview of the ScreenPep™ platform.
Setting new benchmarks in drug discovery
DIA-MS-based techniques are driving the paradigm shift towards next-generation proteomics. These fragment-based approaches are setting new benchmarks in drug discovery, enabling the discovery of innovative drug modalities, including covalent and reversible inhibitors, for challenging disease targets across the proteome.
Evotec is at the forefront of proteomics research, with one of the largest, high-end mass spectrometry facilities in the world. Advanced platforms – like HT-ABPP, HT-PALMS, and ScreenPepTM – are combined with a team of cross-disciplinary experts, and over 25 years of experience in the field. These industry-leading capabilities are transforming modern medicine, discovering novel ligand-target interactions with unmatched precision, depth, and quality.